Table of Contents
What Is A MEMS Microphone? (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems)
In today’s world of smartphones, smart speakers, and wearables, microphones play a crucial role in how we interact with technology. One type of microphone that has become the backbone of modern audio capture is the MEMS microphone. But what exactly is a MEMS microphone, how does it work, and why is it so widely used? Let’s break it down.
What Is a MEMS Microphone?
MEMS stands for Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems. These are tiny devices that combine mechanical and electrical components at a microscopic scale. A MEMS microphone, therefore, is a miniature microphone built using semiconductor manufacturing techniques, similar to how computer chips are made.
Unlike traditional microphones that use larger diaphragms and components, MEMS microphones are etched onto silicon wafers, allowing them to be extremely small, reliable, and power-efficient — perfect for modern consumer electronics.
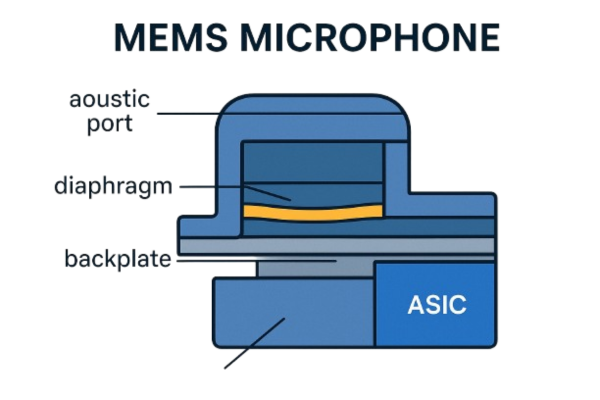
How Does a MEMS Microphone Work?
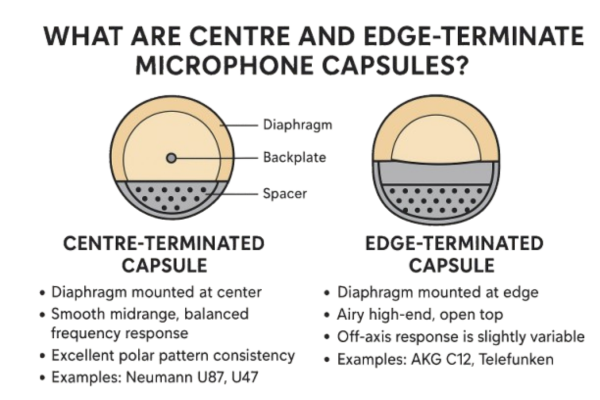
At the heart of a MEMS microphone is a diaphragm and a backplate, much like a condenser microphone. Here’s the simplified process:
Sound waves enter through a small acoustic port.
These waves cause the diaphragm to vibrate.
The changing distance between the diaphragm and backplate alters capacitance.
This variation is converted into an electrical signal.
A built-in ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) amplifies and conditions this signal, producing either an analog or digital output depending on the design.
Analog vs Digital MEMS Microphones
Analog MEMS Microphones: Output a continuous electrical signal. They require external analog-to-digital conversion for digital devices.
Digital MEMS Microphones: Include an integrated ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) and output signals in digital form (often PDM or I²S), making them easier to integrate with processors.
Digital MEMS microphones are more common in modern gadgets due to their noise immunity and simplified design.
Advantages of MEMS Microphones
Miniaturization –
Extremely small size, ideal for slim devices like smartphones and earbuds.
Consistency –
Manufactured with semiconductor processes, ensuring high reliability and uniform performance.
Low Power Consumption –
Perfect for battery-powered devices.
Durability –
Resistant to heat, vibration, and electromagnetic interference.
Scalability –
Easily integrated into arrays for applications like beamforming and noise cancellation.
Applications of MEMS Microphones
MEMS microphones are everywhere, powering the voice-driven world we live in:
Smartphones & Tablets –
For voice calls, recording, and AI assistants.
Wearables –
Smartwatches, earbuds, and fitness trackers.
Smart Home Devices –
Voice-controlled assistants, smart speakers, and IoT devices.
Automotive –
Hands-free communication, noise control, and voice commands.
Hearing Aids & Medical Devices –
Compact size and efficiency make them ideal for healthcare applications.
Conclusion
MEMS microphones have revolutionized how sound is captured in consumer and industrial electronics. Their tiny size, durability, and power efficiency make them indispensable for the voice-first technologies of today and the future.