Table of Contents
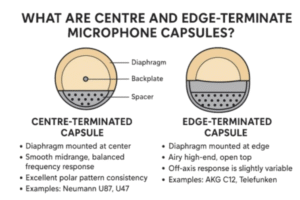
What Are Centre And Edge-Terminated Microphone Capsules?
When it comes to microphones, small design details can make a big difference in how sound is captured. One such detail lies deep within the microphone capsule — specifically, where the diaphragm is mounted. This leads us to two key capsule designs: centre-terminated and edge-terminated.
While the difference might sound technical, it directly affects the mic’s sound character, polar pattern stability, and frequency response. Let’s break down what these terms mean and why they matter.
Understanding the Microphone Capsule
At the heart of every condenser microphone lies the capsule — a small, precise assembly that converts sound waves into an electrical signal.
A typical capsule consists of:
- A diaphragm (a thin, electrically conductive film)
- A backplate (a solid, perforated metal disc)
- A spacer separating the two
Sound waves cause the diaphragm to move, changing the distance between it and the backplate — this variation produces the electrical signal that becomes audio.
Now, how the diaphragm is mounted or tensioned determines whether the capsule is centre-terminated or edge-terminated.
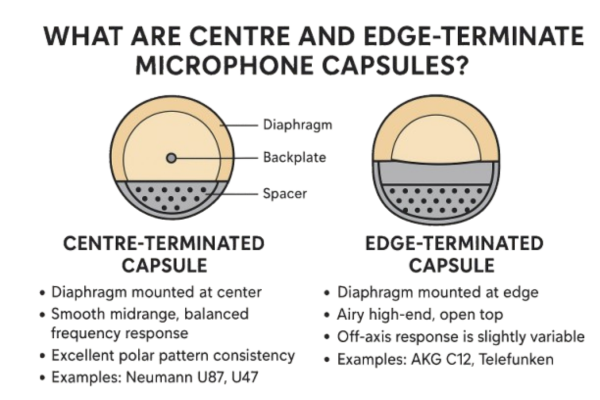
What Is a Centre-Terminated Capsule?
A centre-terminated capsule has its diaphragm mounted and tensioned in the middle, typically held in place by a central screw or ring.
Examples:
- Neumann’s classic U87 and U47 microphones
- AKG’s C414 in some models
Characteristics:
- Tends to produce a smooth midrange and balanced frequency response.
- Often designed for multi-pattern microphones (cardioid, omni, figure-8).
- Offers excellent polar pattern consistency across frequencies.
Because the diaphragm is fixed at the center, it moves more symmetrically, providing accurate phase response and a natural tone — ideal for vocals and studio recording.
What Is an Edge-Terminated Capsule?
In an edge-terminated capsule, the diaphragm is attached around its outer edge, leaving the center free to move.
Examples:
- AKG’s classic CK12 capsule
- Telefunken and various modern boutique condenser mics
Characteristics:
- Tends to offer a more open high-end and airy top.
- Slightly different off-axis response — often considered more musical or natural in ambient recordings.
- The design allows for a larger effective diaphragm area, which can increase sensitivity and tonal richness.
Edge-terminated capsules are often preferred for instrument miking, room ambience, and audiophile recordings where detail and airiness are prized.
Centre vs. Edge-Terminated: Key Differences
| Feature | Centre-Terminated Capsule | Edge-Terminated Capsule |
| Mounting Point | Diaphragm fixed at center | Diaphragm fixed at edge |
| Sound Character | Balanced, smooth mids | Airy, open highs |
| Polar Pattern Stability | Very consistent | Slightly variable off-axis |
| Common Use | Vocals, studio mics | Instruments, ambient mics |
| Examples | Neumann U87, U47 | AKG C12, Telefunken ELA M 251 |
Why Capsule Design Matters
The choice between centre and edge termination isn’t just aesthetic — it’s a matter of acoustic behavior and design philosophy.
- Centre-terminated designs focus on precision, neutrality, and pattern accuracy — great for versatile studio use.
- Edge-terminated designs lean toward character, warmth, and openness — ideal when musicality takes priority.
Microphone designers choose one over the other depending on the intended tone, application, and brand signature.
Final Thoughts
Centre and edge-terminated microphone capsules may look similar from the outside, but their internal geometry shapes the very soul of the sound.
Whether you prefer the neutral accuracy of centre-terminated capsules or the open, musical quality of edge-terminated ones, understanding these differences can help you choose the right microphone for your sound.